The Piping Profile in general can be considered
as a complex and rigid piping network consisting of various piping
components, which have different diameters and weights. At the same time the
above network is also subjected
to temperature change.
A satisfactory design of the Piping System should therefore give a careful consideration to achieve the above requirement. This is generally accomplished by providing external attachments (known as pipe supports) at various locations of the piping profile.
PURPOSE OF PIPE SUPPORTS
TO SUPPORT WEIGHT OF PIPE-DURING OPERATION
& TESTING
Supports are required to support the line during
all conditions i.e. during operation as well as during testing. In case of vapour line this difference will be very large due to hydro testing. Supports
should be designed for this load
Some times line is capable of having longer span but load coming on the support may be very large (especially with large dia pipe lines). Then to distribute the load uniformly, more number of supports should be provided with smaller span.
TO TAKE 'EXPANSION
LOAD'
TO TAKE 'WIND LOAD'
Wind introduces lateral load on the line. This load is considerable especially on large diameter pipe. This tends to sway the line from its normal position and line must be supported guided against it. In case of large diameter overhead lines, supported by tall support extended from floor, wind load introduces large bending moment and should be considered critically.
TO TAKE 'EARTH QUAKE
LOAD'
The earthquake is normally associated with horizontal acceleration of the order of 1 to 3 m/sec2. This is around 10% to 30% of the gravitational
acceleration and introduces horizontal force of about 10 to 30% of the
vertical load (or supported mass). While designing support this should be taken care.
TO ABSORB 'VIBRATION
OF PIPING SYSTEM'
When the pipe is subjected to moving machinery or pulsating flow or very high velocity flow, pipe may start vibrating vigorously and ultimately may fail, particularly if span is large. To avoid this it may be required to introduce additional supports at smaller span apart from other requirements. It may not take axial load, but must control lateral movements.
TO HAVE 'NOISE CONTROL
In most of the plants, noise is resulting from vibration and if such vibrations are controlled, noise is reduced to great extent. In such lines, between clamp (i.e. support) and pipe, asbestos cloth is put to absorb vibration and avoid noise.
TO TAKE 'HYDRAULIC
THRUST IN PIPING
The hydraulic thrust in the pipeline is present at certain point such as pressure reducing valve, relief valve, bellows etc.
If the control
valve has large pressure differential and line size is more, then this force can be very high. The support should
be provided and designed to take this load, otherwise this will load the piping
system and may cause
failure.


TO SUPPORT THE SYSTEM
DURING 'TRANSIENT PERIOD OF PLANT AND STANDBY CONDITION
Transient condition refers to the start-up or
shutdown condition in which one equipment may get heated up faster and other one get heated
slower. Due to this the expansion of one equipment which in normal operation will get nullified, may not get nullified and exert thermal
load on supports.

Standby condition is also similar. If there are
two pumps, one being standby and both connected in parallel (as shown),
design and operating
temp. of both the connections will be same.
But the expansion of two parallel legs will not be nullified
because at a time only one leg will be hot and another being cold.
TO SUPPORT THE SYSTEM
DURING 'MAINTENANCE CONDITIONS'
When for maintenance certain equipment or
component like valve is taken out, remaining system should not be
left out unsupported.
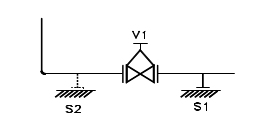
Referring to the FIG, support 'S1' will be
sufficient but when valve 'V1' is taken out for maintenance there will
not be any support for vertical leg. Therefore second support 'S2' may be
required to take care of such condition.
TO SUPPORT THE SYSTEM
DURING 'SHUTDOWN CONDITIONS
In shutdown condition all equipment may not be in the same condition
as in operating condition.

For example, refer the pump
discharge line in FIG, Point A is resting, Point B & C are spring supports and Point D is the pump discharge nozzle. The springs
are, designed based
on weights considering the weight of fluid as
well as pipeline and thermal movements. But during shutdown condition the fluid
may be drained and the pipe becomes lighter. Hence the spring will give
upward reaction and shall load the nozzle 'D' beyond permissible limit.
TO SUPPORT THE SYSTEM FOR ERECTION CONDITIONS
Erection condition can be different than the
operating condition which should be considered while designing supports.
Erection condition can be different than the
operating condition which should be considered while designing supports.


For example for normal operation a long vessel
supported by three supports, S1, S2 & S3 is
shown in FIG-5.
If support S2 is higher, than all load will act at S2 only. During erection if
level of S2 is lower then entire load will be divided
into two supports
S1, S2 only. Therefore foundation of S1, S2 & S3 should be capable
of taking such conditions.

A pipe line supported by S1, S2 & S3 taken
from vessel is shown in above FIG - 6. During operation there will be no weight at S2 & S3 (as it is only guide), but wind condition
will be there. Loads due to such conditions must be considered while designing the supports.
CLASSIFICATION OF PIPE SUPPORTS
Broadly the pipe supports are
classified in three groups as per following details / functions :
General details
Construction
details
Functions ie.
purpose
CLASSIFICATION AS PER
GENERAL DETAILS
A pipe line need to be supported from a
foundation or an structure. The piping loads will be acting on these foundations
/ structures. Since these foundations / structures are built on ground, they
will exert an equal and opposite reaction, while supporting the pipe. In a pipe support, there will be some parts of
support arrangement which is directly attached to the pipeline and there will be some other parts which shall be directly attached to the foundation / structure supporting
the pipe.
As per this general
detail the support
is classified as :
PRIMARY SUPPORTS :
It is the parts of support
assembly which is directly connected to the pipe.
SECONDARY SUPPORTS :
It is the parts of support assembly which is directly connected
to the foundation / structure
and is supporting the primary
support attached to the pipe line.
CLASSIFICATION AS PER CONSTRUCTION :
Based on construction details,
pipe supports are broadly classified in three types,
as
-
RIGID SUPPORTS
-
ELASTIC SUPPORTS
-
ADJUSTABLE SUPPORTS
These are described below in brief.
RIGID SUPPORTS
:
This type of support arrangement is generally
very simple and has maximum use in piping. It does not have adjustibility to
the erection tolerances. It will directly rest on foundation or structure which
is supporting the pipe. Common type of RIGID SUPPORTS are shoe
type (welded), shoe type (with clamp) Trunnion
type, valve holder type, support
brackets (Secondary Support). These are described under the topic 'Supports
Generally used'.
ELASTIC SUPPORT :
This type of support is commonly
used for supporting hot piping.
It shall be able to support pipes even when the pipe is moving up or down at support point.
Common type of elastic supports are variable
type spring supports, constant type spring supports. These are described
under the topic 'Supports generally used '.
ADJUSTABLE SUPPORTS :
This type of support is Rigid type in construction but is has few nuts and bolts arrangements for adjusting the supports with respect to the actual erected condition
of pipe. The support can be adjusted for the erection tolerances
in the piping. These are required for a better supporting needs
at critical locations
of pipe supports.
Mostly all type of rigid supports can be modified
by using certain type of nuts and bolts arrangement, to make it as an Adjustable support.
Only a typical type of
adjustable support is described under the topic 'Supports Generally used.'
CLASSIFICATION AS PER
FUNCTION (i.e. PURPOSE)

Pipe supports classified as per functions are
summarised in the Table.. These are shown along with its basic
construction, the symbols
generally used and type of restraints it offers to the piping
system.
The supports classified as per function
are further described as follows :
LOOSE SUPPORT
:
This is most commonly used support meant for
supporting only the pipe weight vertically. It allows pipe to move in axial as well as transverse direction
but restricts only the vertical
downward movement.
LONGITUDINAL GUIDE :
This type of support is used to restrict the movement of pipe in transverse direction
i.e. perpendicular to length of pipe but allow movement
in longitudinal direction. This is also a commonly
used type of support.
Generally it is used along with Loose support.
TRANSVERSE GUIDE :
This type of support is used to restrict the
movement of pipe in longitudinal (axial ) direction but allows the pipe
to move in transverse direction. This is also referred as 'AXIAL STOP'. This
type is less used as compared to above two types. Generally it is
used along with Loose support.
FIXED POINT / ANCHOR :
FIX POINT type of support is used to restrict
movements in all three directions.
ANCHOR type of support is used to restirct movement in all three
directions and rotation also in these three
directions.
Non-Welded Type (FIX POINT) :
This can be considered as a combination of longitudinal and transverse guide.
This type resist
only the linear movements in all directions but not the rotational movements. This avoids heavy loading of support as well
as pipe. Therefore this type of support is preferred over welded type.
Welded Type (ANCHOR)
This type of support prevents total movements
i.e. linear as well as rotational. This type of support is used when it is absolutely essential to prevent
any moment/force being transferred further.
It causes heavy loading
on support as well as pipe.
LIMIT STOP :
As name itself
indicates it allows
pipe movement freely upto a certain limit and restricts any further movement.
This is useful
when total stops causes excessive loading on piping
and support or nozzle.
This type of support should be used selectively, because
of stringent and complicated requirements of design, erection and operation.
SPECIAL SUPPORTS :
When we need a pipe support
whose construction or functional details
are different from the available details, then a special support detail sketch is prepared. The
functions of this support can be any combination
of above functions.
SUPORT DETAILS
GENERALLY USED :
Following are the type of supports
generally used in a project.
SHOE TYPE SUPPORT :

Shoe type support are the supports used maximum in any project.
These can be directly welded to pipe or can be welded
to a clamp put around
pipe. Shoe type supports are used for supporting lines with insulations.
Basically the detail is as follows :
Basically it is used as a Loose support. With slight addition of details it can be also used as a guide, fix point, anchor, transverse guide, limit
stops. It can also be modified to be used as Adjustable supports.
These are primary supports
and will be supported on secondary supports
(i.e. Foundation or structure)
TRUNNION SUPPORTS :


In this type of support,
a dummy pipe is welded
to the main line so that the dummy pipe becomes a rigid part of
the main pipe line. Now this pipe is suitably supported on a secondary support
(Foundation or a structure) The basic detail is as follows :
As per piping requirement, the TRUNNIONS can be
VERTICLE (as shown in FIG-9) or can also be in HORIZONTAL. These are used for loose
supports, guides, transverse guides, fix points, achors as well as adjustable supports.
HANGER SUPPORT
:


As the name suggest,
in a hanger suport the pipe is hung from an structure
using a hanger rod.
As is clear from the FIG.-10, pipe can move in
all direction except downwards. A hanger support generally uses a clamp
on the pipe. When a turn buckle is used than the support is adjustable type.
Hanger rods are used as a loose supports, which is free to lift up.
SPRING SUPPORT
:
Spring Support is a special
type of support which is used in the situations where the support
point on the pipe is expected to move up or down during the operating condition
(due to thermal growth ) from its installed position without spring, the pipe will
therefore either lift from secondary support or will make an unsuccessful
attempt to press against the rigid secondary support. Both are detrimental to
the structural integrity of the Piping System.
The spring support basically employs a spring
element, which can get compressed or open up depending upon the thermal movement at the support
point of pipe. By doing so it takes the vertical load of the piping under
both the situations. From the utility point, spring supports are classified as
Variable spring type & constant spring type. As per arrangement
spring support can be classified as supporting the pipe from under (i.e resting
type) or as supporting the pipe from above (i.e.
hanger type).
VARIABLE SPRING SUPPORT :
This basically consists
of spring which can get compressed or expanded according
to thermal expansion. However this movement causes increase or decrease in supporting
force depending on its stiffness and this differential load is transferred to the
pipe, but this is much less than that would be with rigid support or rigid hanger.
HANGER TYPE (VARIABLE)
In hanger type variable spring
support, the pipe is hung from the secondary support
using hanger type spring, as shown.
CONSTANT SPRING SUPPORTS :
In variable spring support variability factor
is maintained generally within 25%. When the vertical movement of support
point is large and/or a very less magnitude of differential force from cold to hot condition
is permissible, then constant type of support is used. This is also basically
spring support but load is supported by it through
a lever mechanism in such a way that when spring gets compressed effective leverage is reduced and vice-versa. So that net supporting force
remains constant, i.e. without any load fluctuation.
ADJUSTABLE SUPPORT :
As the name suggest, this type of support is capable of adjustment at site to accommodate erection
tolerances of piping. Basically
all type of support can be easily modified and made adjustable. A typical
example for support at pump suction is shown below.


U-BOLT TYPE SUPPORT :
U-bolt type support
is one of the most simplest and extensively used primary support
item for supporting un- insulated piping.
These are generally
used as GUIDES. These can be used conveniently as fix points for smaller
size, non- insulated piping. For large dia pipes, its
use as fix point is generally avoided.
SPECIAL SUPPORTING
CASES
Few special supporting cases near pumps, tall vessels and exchangers are described as follows :
1.To avoid loading of suction nozzle due to control valve weight, which is nearby, if we provide a trunnion (non insulated as per normal practice) to take weight of control valve, then during operation such nozzle will move up and lift the trunnion off its base. This will load the nozzle and purpose of trunnion will not get served.

2.This can be avoided by insulating trunnion, so
that it will remain hot and will expand upwards and will provide resting.
Thus in most cases, the nozzle loading
can be controlled without use of spring supports, near pump nozzles.


3.When supporting a line coming from top nozzle of a short vessel as shown in , if the temperature and material of the vessel and pipe line is same, then the line may be supported at ground level.

When supporting a line coming from a tall vessel
and the line temperature is different from vessel, it should be supported from
vessel at the neutral point with respect to vessel. Such point is normally near
the nozzle itself The pump
should be connected through flexible loop connection to avoid nozzle loading.
Alternatively
line may be supported at bottom (near pump) and loop may be provided
at top as shown in FIG.
4.While supporting suction and discharge piping
to a pump, the supports being provided should be sufficient to take care the maintenance requirements of
the pumps i.e. if the valves / strainers, on the pumps are taken out for maintenance, the lines should
remain supported.



5. In
comparatively larger size pipes when a resting support is required at location
"A", then an adjustable type supports should be provided. This is
necessary due to the maintenance requirements - such as changing of gaskets,
etc.

FIXED SADDLE LOCATION FOR EXCHANGERS
A horizontal equipment will normally have two supports, saddle type. Normally one of them is made fixed and the other sliding type.Enclosed sketch showing a few typical cases will make the concept clear.
1.For the long vessel as shown in figure 28, selection of fixed saddle is decided by stiff connection 'A'. Now if pumps are located at 'B' then expansion of 15mm (vessel expansion) and 5mm (pump line expansion) i.e. total 20mm will load the pump nozzle excessively.

If pumps are located at 'C' then expansion of the pump line will nullify the vessel expansion, since both are in the same direction
hence this type of arrangement should be preferred if possible.
2.In such case if saddle 'A' is fixed in figure 29, total expansion
of 13m will be required
to be absorbed by pipe line.


If saddle 'B' is fixed
then vessel expansion of 4m will be nullified by pipeline expansion of 4m and only differential expansion of 9 m will be
required to be absorbed.
3.In such case by looking at line size in figure
30, one may think that more attention be given to 20" connection. But
looking correctly, saddle selection does not make any difference as both are at
equal distance from 20" pipe line. Then
selection should be based in favour of 8" pump line i.e. saddle 'B' should be
fixed to reduce load on the pump.


Where ever it is possible to make a flexible
piping to the pump, then in such situations, it is possible to make both
the saddles, SLIDING type.
In conclusion fixed
saddle should be so chosen
that expansion of vessel towards
sliding saddle tends
to nullify or substantially
reduce differential expansion passed onto connected pipe line. Fixed saddle should be close to stiff piping
connections to the equipment.

Nice Blog! Helpful for Industrial noise control and solution!
ReplyDeleteAcoustic treatment wa
Nice Post!!
ReplyDeletePlease Look Here At - Push-Fit Pipeline Solutions are revolutionizing the way industries in India approach fluid and air transfer systems. These advanced pipeline solutions are designed to deliver maximum efficiency, ensuring fast installation and long-term reliability. With no need for welding, threading, or special tools, push-fit technology saves both time and cost while maintaining durability. Businesses in India increasingly prefer this solution for its flexibility and ease of use.