Compressors are normally
located inside a permanent shelter or building (Compressor House) for weather
protection. The compressor house can be fully covered by side cladding to grade
level if handling non-hazardous materials e.g. air.
For compressor, handling
flammable materials, ventilation and weather protection is assured by significant openings upto 2.5m ht. at grade level
together with roof ventilators.
Except for lighter than air
gases, trenches, pits and similar gas traps should be avoided within gas Compressor House. This will eliminate chances of suffocation or explosion risk due to accumulation of heavy
gases in pits.
For open compressor house, the side cladding on
all sides should be provided upto 1m below crane level.
The general arrangement of compressor house shall consider
the vendor drawings
and vendor recommendation, if any, for space and location of auxiliary units.
For compressor house where a
number of installations from multiple vendors are to be accommodated,
a thorough discussion should be held among the engineers of Piping, Process and Civil discipline to finalize the detail plot plan
of the unit.
The clear space between compressors shall be minimum 1.5m or half width of the compressors. The clearance between
rows of compressor and at the end of each compressor shall be also 1.5m.Built-in maintenance equipment viz. travelling
gantry with overhead crane / monorail with hoist and chain-pulley blocks
as well as the drop-out
areas shall be provided in the compressor house.
The clearance above the
compressor should be at least 3m more than the longest internal part to be removed.
The substantial space
required for lube oil and seal oil consoles shall be taken into consideration to prepare unit plot plan.
RECIPROCATING COMPRESSORS
Reciprocating compressor generates considerable
vibrations due to unbalanced forces, pulsation etc. For this reason,
the reciprocating compressors should be located as close as possible to the grade level.
The building foundation and
the compressor foundation should be separate to avoid transmission of vibrations from compressor to the building structure.
The pulsation dampeners are used to eliminate pulsation
in suction and discharge piping and to separate the source of vibration from the piping system.


The piping arrangement around
the reciprocating compressor should be planned at grade level for ease
of supporting with minimum changes in direction
The grade supports should
be spaced unevenly
to reduce harmonic
motion in the piping.
The piping routed
simply with short
run is less prone to vibration, but at the same time the line should be checked for the flexibility and the
compressor nozzle loadings within the allowable limits furnished
by the vendor.
The piping shall remain clear of the cylinders
and the withdrawal space at cylinder heads.
CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSORS
The general considerations
for centrifugal compressor layout is same as the reciprocating compressor, exception being that for centrifugal compressor, the
pipeline size is larger, temperatures can often be higher and nozzle
loadings on compressor casing is lower.
The knockout pots, interstage
exchangers can be located at grade outside the compressor house with
auxiliary equipment consisting of lubricating, seal and control oil systems be
placed adjacent to the machine.
The centrifugal compressor
inside a building normally have foundations separate from the building foundation.
The centrifugal compressor with drive are
generally mounted on the concrete table supported on RCC column.
The maintenance facilities like overhead crane
or monorail at the centre
of the compressor bay and the drop-out area
at one of the building or shed is the usual
practice.
If the building is having
installation of several compressors, the height of the travelling crane is to be carefully estimated
so the machine components and rotors can be lifted
over the adjacent equipment.
The compressor suction lines must be free of
any foreign particles that could damage the
internals of the machine. Strainers are installed in the inlet line between
the isolation valve and the compressor inlet
nozzle.
ASME PTC code recommends a
minimum 3 times diameter of straight run piping between elbow and
the inlet nozzle.
The designer shall ensure that all connections shown on the vendor piping
and instrumentation diagrams are properly
taken care in the piping layout. All valves shall be arranged in such a way that
they are accessible from the operating floor around the machine.
AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT
Centrifugal and reciprocating
compressors and their drives require a variety of auxiliary equipment to support their operation. The equipment for these
compressors are discussed below.
Lube Oil Consoles: Compressor bearings receive lubricating
oil from the lube oil console. These consoles
may be either stand alone or be mounted directly
onto the compressor frame. The console consists of lube oil reservoir, oil filters, oil coolers and lube oil pumps.
Seal Oil Consoles:
The hydraulic seals located at the outer ends
of the compressor shaft receive oil from the seal oil console. The seal oil console consists
of seal oil reservior, oil filters and main seal oil pumps.
Inlet Filters:
The inlet filters for air compressors are installed outside the building /shed at a level suitable for clean air suction without any obstruction in the air flow. The vendor drawing of the filter shall be reviewed for correct inlet/outlet ducting and the supporting arrangement.
Suction drum / knockout pot :
As compressors require dry
gas free of foreign particles, it is necessary to pass inlet gas through the suction drum or knockout
pot. This vessel
removes moisture and particles from the gas by passing it through a
demister screen located just below the outlet nozzle.
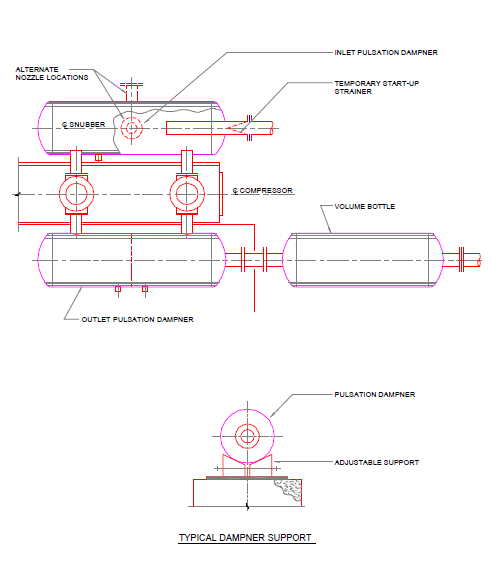
Pulsation dampener / volume bottles:
The negative
effects of vibration on the life of reciprocating compressors and associated piping can
be minimized by the use of pulsation dampeners (Refer Fig.CHP6). The pulsation dampeners are sized by the compressor vendor and are mounted directly
on the cylinder nozzles.
Volume bottles are used to
reduce vibration. They are located downstream of the discharge pulsation dampener and are similar
to snubbers without
internal baffles or choke tubes.



PIPING ARRANGEMENT
The compressor house piping consist of suction
/ discharge piping, auxiliary equipment piping
and utility system
piping. The main suction line with its components shall
be as short and direct
as possible. The discharge line with its main components shall be routed
clearing the compressor and its driver and supported independent of compressor foundation
or building column foundation. This will minimise the
transmission of damaging vibrations to the building structure / frame.
The vendor furnishes that
P&ID for the compressor with its auxiliary equipment. These drawings should be reviewed
fully for the provisions of vents and drains requirement of the installation.
For reciprocating compressors, API 618 provides the acceptance criteria
for nozzle loads. For centrifugal compressors, API 617 provides the acceptance criteria
for nozzle loads.
Reciprocating compressor
piping arrangement should be finalised after analog study which identifies
potentially damaging accoustic or pulsation problems during design phase itself.
I am really interested in what you wrote here. This looks absolutely perfect. All these tinny details gave me a lot of knowledge.
ReplyDeletegas pipeline inspection
The components of a compressor must be developed for usage with compressed air for the Compressed Air Piping Systems to function correctly.
ReplyDeleteDrone pipeline inspection enhances safety and efficiency by using aerial technology to detect leaks, corrosion, and structural issues, providing real-time data for proactive maintenance and repairs.
ReplyDeleteDrone Pipeline Inspection use thermal imaging and AI to detect leaks, corrosion, and structural issues efficiently. Drones like the DJI Mavic 3 Thermal offer high-resolution thermal and visual imaging, long flight times, and RTK precision, ensuring cost-effective, safe, and accurate pipeline monitoring.
ReplyDeleteGood explanation of Reciprocating Air Compressors and their operating principles. We’ve seen them perform reliably in applications with fluctuating demand, mainly because of their straightforward design and ease of maintenance. A useful read for anyone comparing compressor technologies.
ReplyDeleteEfficient Compressed Air Pipework is essential for industries that rely on pneumatic systems for daily operations. In India’s growing manufacturing and processing sectors, a well-designed piping network ensures optimal airflow, minimal pressure drop, and long-term reliability. Modern systems are engineered to deliver consistent performance while reducing energy costs.
ReplyDelete