The study of the tankfarm consisting of a group of tanks shall be carried
out keeping the following basic points in consideration.
1. Grouping of tanks,
2. Specification of the content.
3. Capacity of tanks
4. Nature of hazard - fire
- toxic
- explosive
- corrosive
- bulk handling loading
5. unloading
6. Statutory distance
7. Requirement of Dykewall or curbing
8. Dykewall height or curb height calculation
9. Location of Pumps - inside dyke area
- outside dyke area
10. Approach to tank nozzles with valve
11. Approach to tank roof
12. Drainage of dyke area - Sump and pump
13. Road around tankfarm
14. Fire hydrant / monitor requirement
15. Underground system connected to specific system of treatment / disposal
Storage tanks located in a safe area and grouped according to the contents
are called tankfarm. Normally, in chemical plants, the storage shall be either
input raw material or output products or intermediate chemicals storage.
Storage tanks may contain acids, alkalis, oil viz. petrol, diesel, naptha,
fuel oil or benzene etc. Oil, acid, alkali are usually stored in vertical
storage tanks designed as per API 650.
Tanks should be grouped or segregated according to the contents. Tanks
containing hydrocarbons should be separated according to the flash point, CCE
classification for space planning, dykewall and its height requirement.
Layout of the storage facility shall be based on the following
considerations and systematic approach.
- Statutory Regulations viz. CCE
- TAC/NFPA recommendations
- Safety requirements as per OISD, OSHA, HAZOP study
- Valve access platform / ladders at the piping outlet
nozzles of tank.
- Access to top of tanks and interconnecting walkway
- Piping on sleepers or piperack inside dyke area.
- Pumps location outside dyke area
The practical objective to prepare a most economical plot plan and piping
arrangement for a tankfarm should be to keep provisions of operational ease, maintenance
facility, safety arrangements and overall aesthetics. The tankfarm shall also
have provisions for efficient drainage and disposal facility as required for
various kinds of fluid storage.
The tankfarm should be secured against unauthorised entry by fencing,
security gates depending on the tank storage capacity or the type of hazards
posed by the nature of contents.
Important Terms Related TankFarm
Atmospheric tank - The tank that operates at pressure levels ranging from
atmospheric pressure to 0.5 psig.
Bullet - This is a high pressure horizontal storage vessel shaped like a
bullet.
 |
| High pressure horizontal storage vessel-bullet |
Cone-roof tank - This is a low-pressure vertical storage tank with a
cone-shaped fixed roof.
Fixed roof tank - This is a low pressure vertical storage tank with a roof
welded to the shell
Irrespective of roof design or method of support.
Floating roof tank - A floating roof tank design is adopted to conserve
vapour loss and minimize fire hazard.
 |
| Floating roof tank |
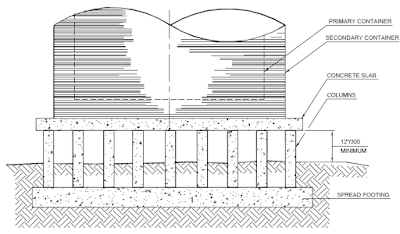
Double-wall storage tank - A double wall storage tank has an inner wall to
contain a liquid, an
annulus space usually filled with insulation and outerwall for containment
of spillage.
Horton sphere - It is a spherical vessel used for storage of high pressure
liquid and gases.
Dyke - A dyke is a barrier designed to contain liquid in the tank in case
of emergency within the area for safety reasons.
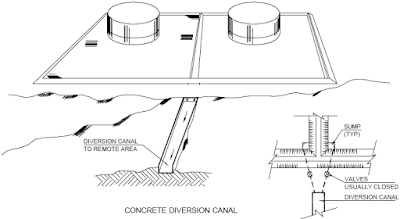
Diversion dyke - This is a barrier designed to divert spillage from other
storage tanks. It uses
natural terrain to direct liquids to the sump area.
Flame arrester - In the event of lightning or another source of vapour
ignition, a flame arrester in the vent line of a storage tank prevents flames
from flashing to the vapour inside the tank.
Breather valve - This is provided as a measure to protect the tank against
collapse due to sudden creation of vacuum inside the tank during suction by
pumps.
Foot valve - This valve is provided at the bottom of a riser in a tank
where a submersible pump can be installed. During regular operation, foot valve
remains open.
Sleeper - Sleepers are steel or concrete supports usually located within
450mm of grade of piping systems commonly found in offsites.
Sump - This is the low point basin within an area used for collection of liquid
waste for disposal.
Foam - This is a
solution with a density lower than that of oil and water. It is used to form a
blanket over dangerous vapours and reduce the risk of explosion.
BUND AREA TO CONTAIN SPILLAGE
The risk of failure of storage tanks and the primary piping systems is
reduced to certain extent, if the fluid is contained within the bund wall and
is not allowed to spread throughout the area resulting in various hazards like
fire, toxic spread, pollution problem etc.
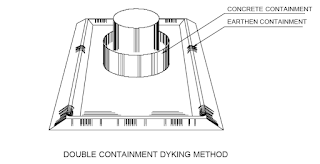
The dyke may be constructed of earth, concrete, solid masonry or steel. It
may be square, Rectangular, circular or irregular in shape, conforming to the
natural terrain around the tank.
The containment dyke for tankfarm under the purview of chief controller of
explosives (CCE) shall be planned according to the CCE rules and regulations.
CCE rules are applicable to the fluids of petroleum and petroleum products
classified as class A, B or C according to its flash point characteristics.
The rules of CCE can be followed for other hazardous / inflammable products
as good guidelines of safety, even though the product is not classified as
petroleum product.
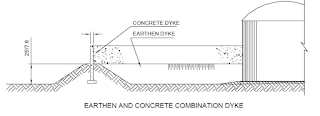
One common method of dyke construction is by earth upto a height of 1.8m
and with width of dyke on top to be about 600mm. The slope on the surface of
dyke is usually 1:1.5 consistent with the angle of repose of earth.
In congested area or where space is limited, usually concrete dyke is made
with varying height for different containment capacity.
The free volume of the bund area is sized to contain the contents of one
largest tank plus a margin of 10 percent.
All drains from the dyke area should be equipped with a valve outside the
dyke regardless of
whether the drainage goes to disposal pit or sewer system. This prevents
liquid spillage from
entering the sewer or released from the dyke area. These valves should be
kept closed and blanked off except when withdrawing water.
The contamination of spillage with the natural rain water or wash water
needs this drainage to be treated before disposal. Depending on the
contamination, the valve can be used for diverting either to storm water system
or to the Effluent Treatment Plant.
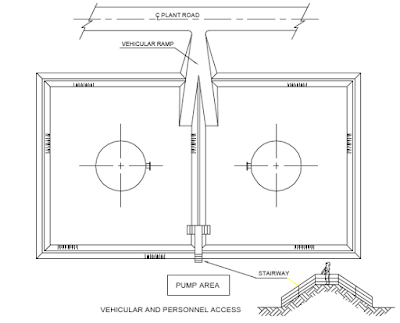
Access to the dyke area is usually provided by making vehicular ramp at one
end and a stepped entry at the other end.
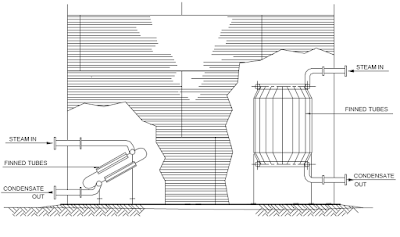
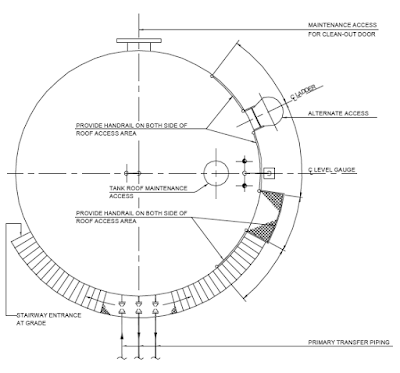
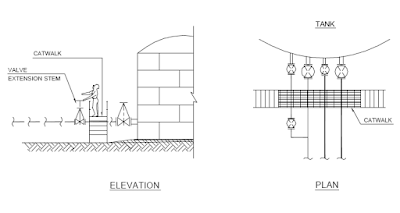
A typical illustration on the top of a vertical storage tank is given in
Fig.
Valve access catwalk, Tank heater installation, Floating Roof Tank access
are illustrated as typical examples.
 |
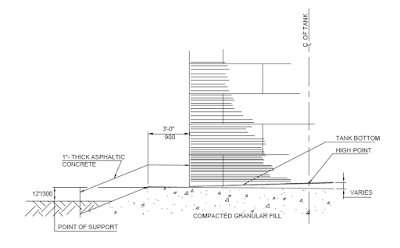
A low temperature tank foundation with elevated concrete base is
illustrated in Fig.
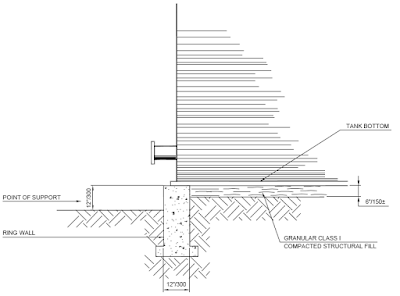
A tank located on compacted granular fill is illustrated in Fig. and
a tank on the ring wall
Foundation is illustrated in Fig.



The way You explaining this chapter was wonderful and nice but for me little confusion about Tank Heater Installation - piping course in chennai
ReplyDeleteThank you so much to share such an amazing article with us. I really enjoyed your article. Keep us updating with more informative articles. Also, Check out Buried Pipe Insulation.
ReplyDeleteImportant blog information, thanks for sharing this article. It really a very good quality Pipe layout. More Details!
ReplyDeleteYour post is very impressive, even a layman can understand. This will certainly help. Thank you for sharing this valuable information. Petroleum storage tank equipment.
ReplyDeleteThank You for sharing this informative blog
ReplyDeleteDo visit our website: Aluminium Bronze Bar Manufacturer & Suppliers
Website: https://dhanwantmetal.com
Thank You for sharing this informative blog
ReplyDeleteVisit our blog: Stainless Steel Flanges
You may also like: Slip on Flanges
Website: https://vihaforge.com
At Ecosphere India, we are dedicated to be industry leaders in the Manufacture of Grain Storage Silos. Our purpose is to provide the farming community with modern, robust and cost-effective designs. Our designs focus on innovation, quality and sustainability of our grain storage silos. Our silos are intended to keep harvested crops fresh longer, waste less of the crop after harvest and enhance the safety of food storage.
ReplyDelete